Nirmala Sitharaman, the Minister of Finance of India, declared that India would begin a mission to eradicate sickle cell anemia by 2047 during her speech on the Union Budget for 2023–2024.
Sitharaman stated that the mission will involve raising awareness, conducting a comprehensive screening of seven crore individuals in the 0–40 age range in the affected tribal areas, and in collaboration with the state government will also provide needed counseling.
We all have heard words like anemia which is a common blood disorder caused due to iron deficiency and now “sickle cell anemia”, which has now become a matter of national interest.
Let’s try to understand it in detail for the sake of good health and social awareness.
What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
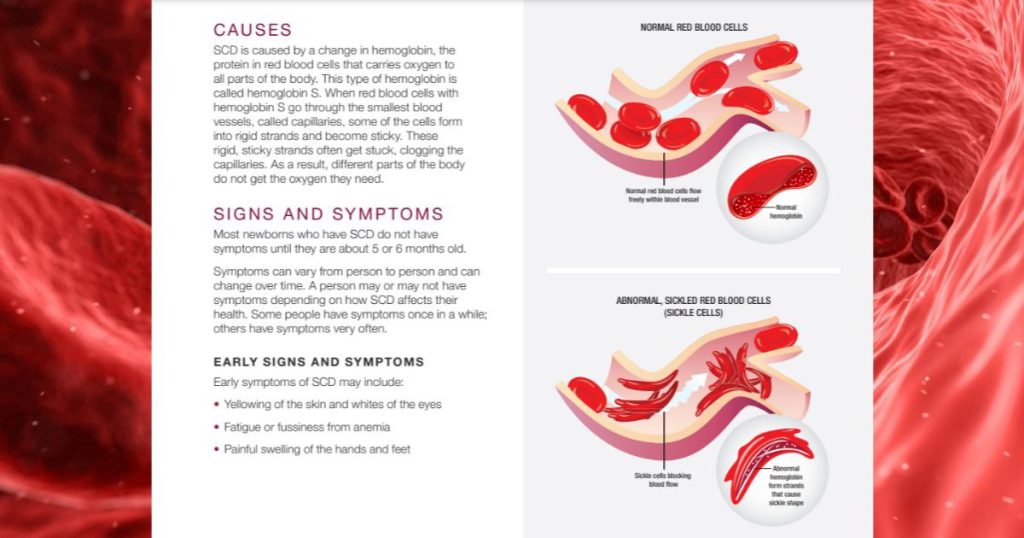
Sickle cell anemia is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders known as Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), affecting the shape of Red Blood Cells (RBCs).
Healthy red blood cells are spherical and flexible, and they contain hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein that transports oxygen from your lungs to all areas of your body via small blood capillaries.
People suffering from sickle cell anemia, have their red blood cells shaped like a C-shaped farm tool called a “sickle” or crescent moon. Over time, these sickle cells also become rigid and sticky, which can slow or block blood flow.
Although there is no cure for most persons with sickle cell anemia, therapies are available to alleviate pain and assist prevent complications.
Also Read| Anemia: 9 Things Doctors Want You to Know
Causes of Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle Cell Anemia is a genetic disorder in which people inherit the illness from their biological parents. It causes mutations or changes in the gene that contributes to the production of healthy red blood cells in the body.
People who have sickle cell anemia get the defective hemoglobin protein gene from both of their biological parents.
If a child inherits the sickle cell gene from only one parent, then that child will have the sickle cell trait, but generally, they don’t exhibit any symptoms. However, because they have the condition, they can carry the gene to their offspring.
The average lifespan of normal red blood cells is 120 days while any sickle cell self-destroy itself in 10 to 20 days. Your bone marrow typically produces enough RBCs to replace dying cells and it behaves like a factory that is striving to balance supply and demand when cells die earlier than expected. You don’t have enough red blood cells if the bone marrow factory can’t keep up.
Symptoms Of Sickle Cell Anemia

Around the age of six months, sickle cell anemia symptoms typically start to show. They can evolve and differ from person to person.
The followings are some signs and symptoms:
- Anemia – Red blood cells typically last for 120 days before needing to be replaced in anemia. However, sickle cells normally expire after 10 to 20 days, which results in a dearth of red blood cells (anemia). The body cannot receive adequate oxygen without enough red blood cells, resulting in weariness.
- Severe and periodic pain – are common signs of sickle cell anemia. Sickle-shaped red blood cells block the flow of blood to your joints, abdomen, and chest, causing pain.
- Swelling of the hands and feet- Due to sickle-shaped red blood cells that are obstructing the blood flow to the hands and feet.
- Regular Infections – Sickle cells can harm the spleen, making it more prone to infections. However, life-threatening infections, such as pneumonia in young children and newborns, can be prevented with the right immunization and medications.
- Puberty or delayed growth – Red blood cells give the body the oxygen and nutrition it needs to grow. However, a lack of healthy red blood cells can delay puberty among teens and slow down growth in babies and children.
- Vision Problem – Sickle cells can obstruct the tiny blood vessels that supply the eyes. As a result, vision problems may result from damage to the retina, the part of the eye that processes visual images.
Newborns with sickle cell anemia may go months without displaying any symptoms. However, anemia can be identified by excessive weariness or general discomfort, painfully swollen feet and hands, and jaundice.
Also Read| Was Chinese spy balloon taken down by the US? Here’s what happened
Who is mostly affected by Sickle Cell Anemia?
Millions of people worldwide suffer from sickle cell disease (SCD), which is more prevalent among those whose ancestors originated in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East or Saudi Arabia, India, and Mediterranean nations like Turkey, Greece, and Italy. It is also more prevalent in Spanish-speaking areas of the Western Hemisphere (South America, the Caribbean, and Central America).
Some data also suggest people with sickle cell anemia are typically those whose ancestry can be traced to regions of the world where malaria is common and who also inherit a gene that offers only partial protection from anemia.
Also Read| All you Need To Know About Norovirus
Prevention Of Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disorder. A blood test can determine whether you have the sickle cell trait, which you might pass on to your offspring. Without having sickle cell disease or sickle cell anemia, a person can have sickle cell trait.
Treatment and Cure For Sickle Cell Anemia
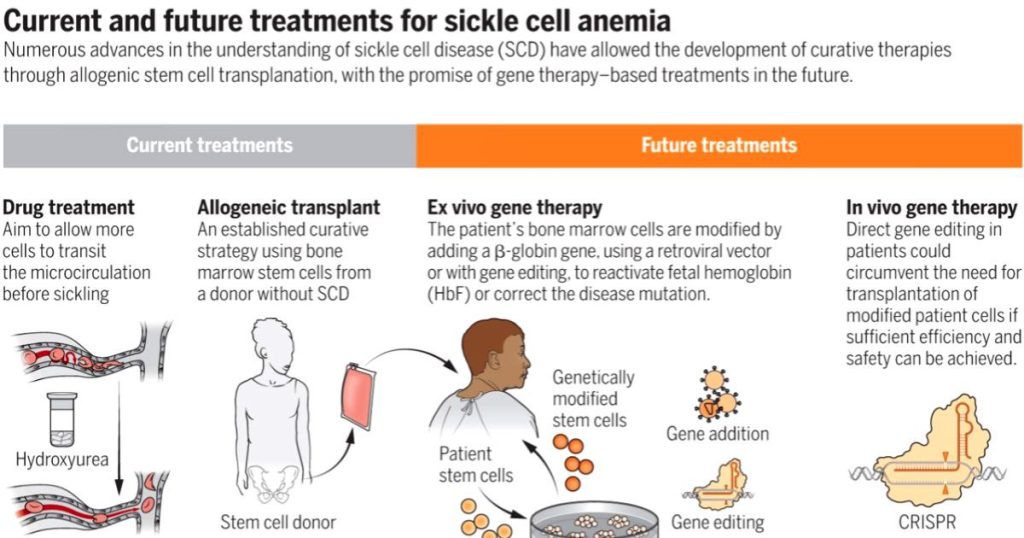
Blood transfusions are commonly used to treat sickle cell anemia, as well as antibiotics and medicines to treat infections that alleviate symptoms caused by sickle cell anemia complications.
A bone marrow or stem cell transplant is the only treatment recognized by the FDA as having the potential to treat SCD.
Bone marrow or stem cell transplants are associated with a high risk of serious side effects, including death. For the transplant to succeed, the bone marrow must be a close match. The ideal donor is typically a sibling. These transplants are typically performed on children who have severe cases of SCD.
Blood cells are created in the soft, fatty tissue called bone marrow, which is located in the core of the bones. A bone marrow or stem cell transplant involves taking healthy blood-forming cells from one person—the donor—and transferring them to a patient whose bone marrow isn’t functioning properly.
Also Read| Sickle Cell Disease Support Corner (Ministry of Tribal Affairs)
Life Expectancy Of Sickle Cell Anemia Patient

Earlier new babies born with sickle cell anemia seldom survive past the age of 5. Today, medical professionals can identify sickle cell at an early stage and can start treatment to reduce symptoms and problems.
Nowadays, sickle cell anemia patients are living longer and enjoying a higher quality of life thanks to medical professionals and novel treatments. People with sickle cell anemia today often live into their 50s.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides the following recommendations for people with sickle cell anemia:
- Get regular checkups and good medical care.
- Maintain your mental well-being because the stigma connected with it might lead to depression.
- Consume a balanced healthy diet and drink plenty of water.
- Avoid becoming overheated or under-cooled by maintaining a healthy body temperature.
- Do regular exercise, as it improves your mood and overall health.
- Participating in a clinical trial could be a means for you to receive novel medications and treatments through your doctor.

Today’s newborns are likely to survive well into their 50s. Medical experts may now manage sickle cell anemia as a chronic illness thanks to advances in research. It is an illness, nevertheless, with important, and occasionally fatal, medical ramifications. Even today, Researchers and healthcare workers are working tirelessly to develop a cure for sickle cell anemia.










Although todays newborn are likely to survive well in their 50s but only medical success in treating various genetic diseases and fighting contagious- non contagious is not enough. As we used to listen to our fathers telling us stories of how they saw their fore fathers of 100+ age when they were little ones makes us to face the harsh reality. Will our children be even able to see the faces of their grand-parents. The daily routine, diet and the environment in which we are prevailing snatches from us our age of living. Every 4 in 5 people are suffering from either hypertension or diabetes. All i want to convey is a little towards environment , a little with the help of medical facilities and a little with our daily routine will aid in having a healthy life.